What is Pixel Binning?
Pixel Binning is a photographic technique that merges multiple adjacent pixels of the image sensor into one large “superpixel” to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. It helps capturing cleaner and brighter low light images by keeping the noise level low.
In case of an image sensor, pixels refer to the light sensitive elements that captures light information and converts them into electrical signals.
Why is pixel binning so important for smartphones?
Generally, sensors with larger pixels perform better as they can capture more light information. Using larger pixels increases the sensor size, and having more of them increases the size even further. Smartphone manufacturers these days seem to be on a mission to reach the sky with the pixel count (i.e., the resolution) of the image sensors.
However, we cannot go above and beyond when it comes to the sensor size of a smartphone, because it would increase the focal length of the camera assembly to a point where the camera module would look like a separate lens from a professional camera! And you definitely don’t want that to happen.

In order to have more pixels within a not-so-large sensor, the pixel size needs to be shrunk down. Now, this reduces the light absorption of the pixels, resulting in poor performance, especially in low-lit situations.
This is where pixel binning enters the game. It allows manufacturers to brag about the resolution while maintaining the signal-to-noise ratio of the pixels.
Quality improvements we get with pixel binning –
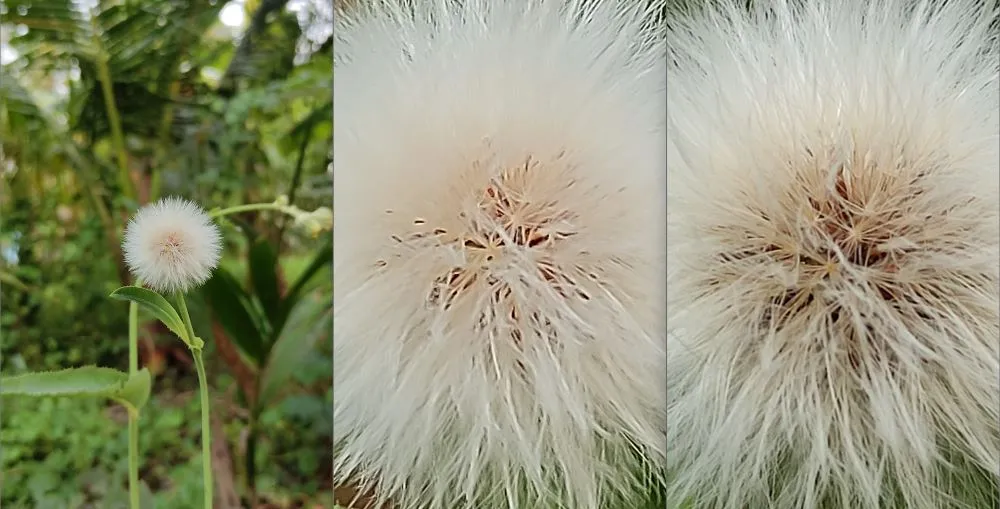

The low resolution binned shot appears clearer and more detailed because each simulated larger pixel collects more accurate information about the subject.
I took the image samples from a low end device to avoid computational processing enhancements in binned shots. Because many of the computational processing enhancements are mistaken as the blessings of pixel binning by most people.
How pixel binning improves smartphone photography?
Since the pixels can’t differentiate between colors, a color filter array is used in front of the sensor that lets only a specific color to enter a pixel and the data of that pixel indicates that particular color. This is called the bayer filter.
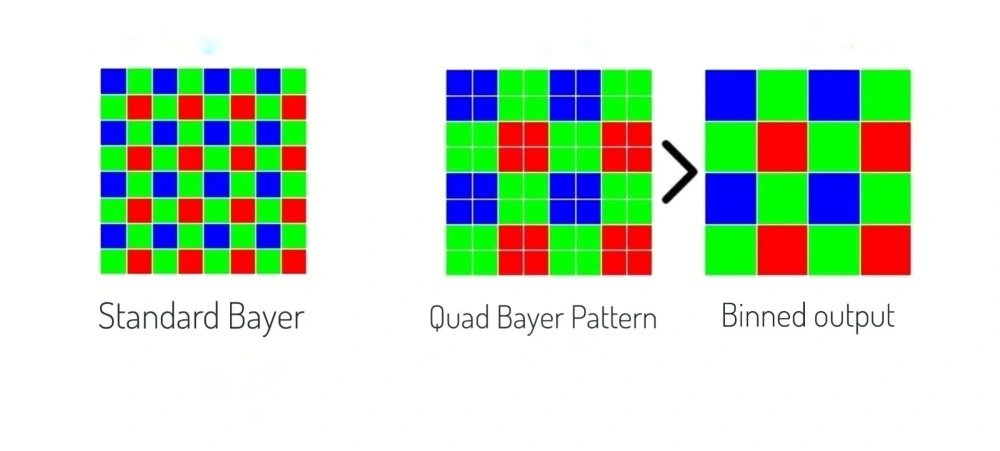
Now, for pixel binning, the arrangement of the color filter array is different than a traditional bayer structure as shown above. The most basic pixel binning method involves combining a 2×2 grid of pixels into one. This requires a single color filter to cover a 2×2 grid of pixels. This is called the ‘quad bayer’ structure.
Values from each cluster of 2×2 pixels are merged together using specific software algorithms. We are basically creating a visualization of one bigger pixel by analyzing the values of a number of pixels (four in this case).
After analyzing the values of multiple adjacent pixels we get a more accurate value that kind of represents a bigger pixel or photosite. This is how pixel binning improves image quality but at the cost of resolution.
Now some of you might asking yourself a question:
How a full resolution image is taken with this quad bayer structure?
Well, a standard bayer pattern has to be recreated from the quad bayer structure. The device takes the individual pixel values from the clusters and remaps them according to their color filters following the pattern of a standard bayer filter. This is achieved by software based array conversion.
When to use pixel binning?
- In low light situations
- When you prioritize a smaller file size.
- The frame is quite simple and doesn’t require that many pixels anyway, such as just a cup of tea.
When you should capture with the full resolution instead?
- The environment is well lit such as outdoor in daylight.
- The frame has a lot of small structures to capture and also sufficient light.
- You are planning to print the image in a size larger than the equivalent of 4k. However the size of the print depends on the ‘dpi’ of the print.
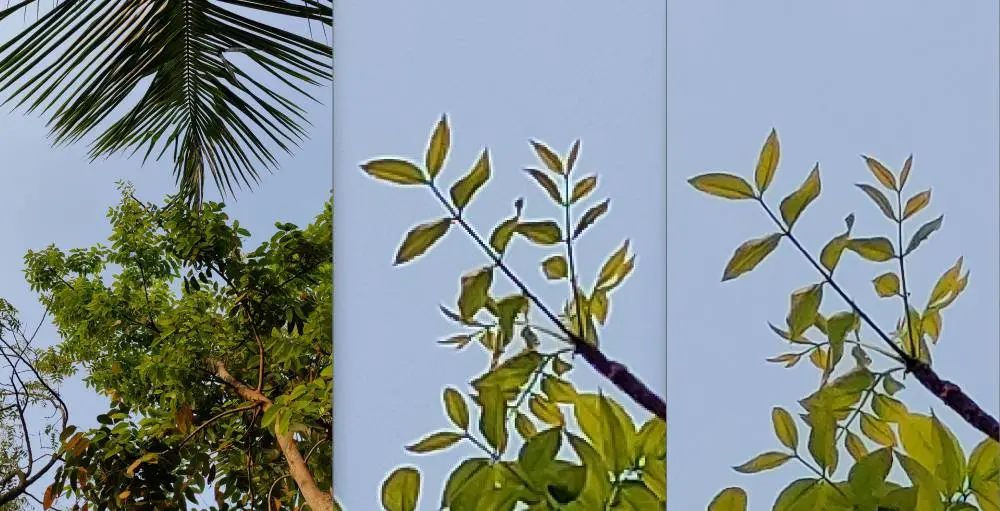

We took two different shots of the same subject, one at binned 16MP and the other at full 64MP respectively in a bright daylight condition. The 64MP sample exhibits better detail, which proves particularly useful when zooming in later.
How pixel binning helps brighten up the low light shots?
In low light, increasing the ISO sensitivity helps taking a brighter image (increasing the exposure time also works but that requires a tripod, and is a different thing). However, increasing the electronic gain results in an increase of the noise or inaccuracy of the signal.
Pixel binning increases the signal-to-noise ratio, thereby reducing the noise. As a result, the system can be operated at a higher ISO, which brightens up the shot in low light while maintaining the same noise level in the final image.
Different pixel binning (CMOS) technologies
- Tetracell or quad pixel binning – merges 4 pixels into one, improves SNR by 2 times
- Nona binning – merges a 3×3 grid of pixels into one, SNR is improved by 3 times
- Tetra2 binning – groups a 4×4 grid of pixels into one, SNR is improved by 4 times
Now you may think why the signal-to-noise ratio improvement isn’t equal to the area of the ‘super-pixels’. For context, a physical pixel with four times larger the size has 4 times higher SNR value than the smaller pixel where binning four pixels together only achieves 2 times SNR improvement.
Well, this is because binning of CMOS sensors are performed outside the sensor after readout of the pixels. Where the readout involves introduction of read noise for all the smaller pixels. So you don’t get quite an uplift in performance like you would get on a physically larger sensor.
Final take
Though pixel binning has its specific contribution in mobile imaging, but there are some misconceptions about pixel binning. It takes more than just binning the smaller pixels to create a nice looking image. It involves the use of computational photography techniques like HDR processing, night mode, using multiple sensors at the same time to grab as much info possible about the shot. Not everything is due to pixel binning.


